Facial Trauma Reconstruction
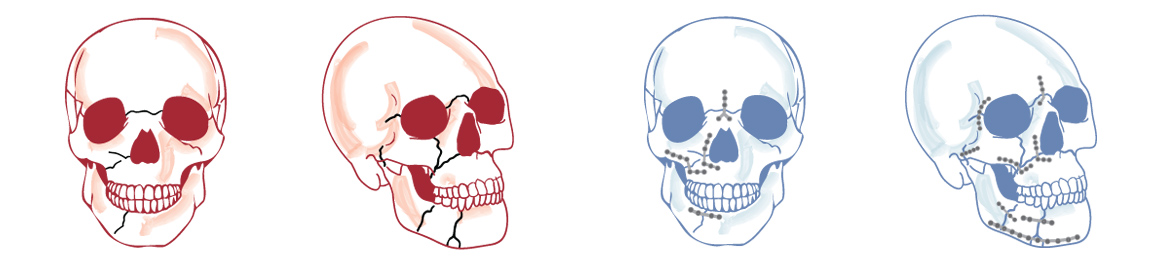
Facial trauma can involve both soft tissue (skin, muscles, nerves, blood vessels) and the bones. Repair of complex facial trauma requires extensive knowledge of anatomy of the face and experience in evaluating and treatment facial trauma. A detailed facial trauma evaluation including examination of all injured areas, all cranial nerve functions, palpation of facial bones, oral and nasal exams, and review of imaging (such as X-ray or Computed tomography, CT, scan) is warranted. In non-isolated trauma (trauma to multiple areas of the body, or high energy trauma), a head to toe examination by the trauma team should be prioritized.
Facial fractures (broken facial bones) can include the nose, the upper or lower jaws, the cheekbones, the eye sockets, the forehead, or a combination. Facial fractures should be repaired within the first two weeks of injury before the broken bones heal in the wrong alignment (malalignment). Untreated or misaligned fracture repair can also be treated in a delay manner; however, osteotomy (re-fracture) at the old fracture sites to allow for repositioning of the bone is necessary. In these complex cases, bone grafting is often to fully restore the malposition fractured pieces back to normal anatomy. The bone grafts are often obtained from the hip bone or the skull bone.
Who is a good candidate for facial trauma reconstruction?
Healthy patients who are not in critical condition due to their traumas are candidates for reconstruction. In multi-trauma cases, reconstruction must be delayed until the patient’s condition is optimized and they are safe to proceed with complex reconstructive surgery.
How is the surgery performed?
There are different approaches for different type of fractures but in general they are either through the existing facial lacerations and well hidden incisions inside the mouth, along the eyelid crease, or along the hairline. If facial nerve injury and/or parotid duct injury are suspected, exploration and repair is warranted. If the teeth bearing jaw bone is involved, the jaws may be closed tightly with rubber bands after surgery as part of fracture stabilization.
What is the recovery?
Downtime from a facial trauma reconstruction is generally 1-2 weeks. Bruising and swelling will be greatest in the first week but should resolve in four weeks. If the jaw bones are involved and maxillo-mandibular fixation (jaws tightly bound with rubber bands), patients may lose up to 15 pounds during the recovery period. Pain is expected after surgery and can be controlled with pain relief medications.
Facial laceration repair is one of the most common urgent procedure in plastic surgery. A cut in certain area of the face can involve nerve injury and requires expertise in microsurgical repair to repair the injured nerve and preserve normal facial expression and sensation. Facial laceration should be repaired within 6 hours of injury ideally and up to 24 hours after to minimize risks of infection and tissue necrosis. Delayed repair is possible, but debridement (removal of necrotic tissue) is often necessary. In the face, there are multiple distinct layers (skin, fascia, muscles, etc), repair of all layers involved in the injury is paramount to achieve optimal outcomes.


